How to Measure Electrical Resistance Using Sensors
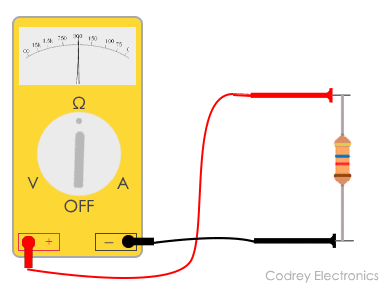
Measuring electrical resistance is an essential aspect of electronic engineering. It allows engineers to determine the flow of current in a circuit and identify potential issues with connections or components. While traditional methods of measuring resistance involve using a multimeter, more advanced techniques utilize sensors to provide accurate and reliable readings.
In this article, we will explore how sensors can be used to measure electrical resistance effectively. We will discuss the types of sensors available, the principles behind their operation, and the steps involved in utilizing them for resistance measurements.
Types of Resistance Sensors
There are several types of sensors that can be used to measure electrical resistance. Some of the most common include:
- Strain Gauges: These sensors change resistance in response to mechanical stress, making them ideal for measuring deformation or strain in structural components.
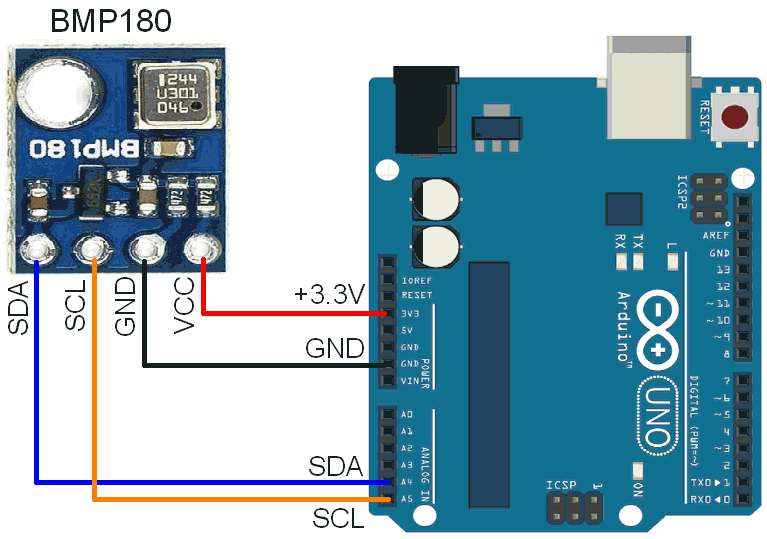
- Temperature Sensors: Certain temperature-sensitive resistors, such as thermistors, can be used to measure electrical resistance based on changes in temperature.
- Pressure Sensors: Some pressure sensors utilize changes in resistance to measure variations in pressure.
- Photoresistors: These sensors change resistance based on the intensity of light hitting them, allowing for measurements related to ambient light levels.
Principles of Operation
The principles behind sensor-based resistance measurements vary depending on the type of sensor being used. However, most sensors operate based on the concept of changing resistance in response to a specific stimulus, such as temperature, pressure, strain, or light.
For example, a strain gauge will exhibit higher resistance when subjected to mechanical stress, while a thermistor will experience changes in resistance based on temperature fluctuations. By measuring these changes in resistance, engineers can derive valuable information about the environment or the object being monitored.
Steps for Measuring Resistance Using Sensors
When utilizing sensors to measure electrical resistance, certain steps must be followed to ensure accurate and reliable results. The following are the general steps involved in measuring resistance using sensors:
- Choose the appropriate sensor for the desired application based on the type of resistance being measured (e.g., strain, temperature, pressure, light).
- Calibrate the sensor to establish a baseline resistance measurement under normal conditions.
- Apply the sensor to the object or environment being monitored, ensuring proper connection and placement.
- Initiate the measurement process and record the resistance readings provided by the sensor.
- Analyze the data obtained from the sensor to draw conclusions about the electrical resistance in the system.
Conclusion
Using sensors to measure electrical resistance offers a convenient and efficient method for monitoring various parameters in electronic systems. By understanding the types of sensors available, the principles of their operation, and the steps involved in utilizing them, engineers can effectively measure resistance and diagnose issues within circuits.
Whether you are working on a complex electronic project or simply troubleshooting a faulty connection, employing sensors for resistance measurements can streamline your process and provide valuable insights into the behavior of electrical systems.
How to Measure Electrical Resistance Using Sensors
Measuring electrical resistance is an essential aspect of electronic engineering. It allows engineers to determine the flow of current in a circuit and identify potential issues with connections or components. While traditional methods of measuring resistance involve using a multimeter, more advanced techniques utilize sensors to provide accurate and reliable readings.
In this article, we will explore how sensors can be used to measure electrical resistance effectively. We will discuss the types of sensors available, the principles behind their operation, and the steps involved in utilizing them for resistance measurements.
Types of Resistance Sensors
There are several types of sensors that can be used to measure electrical resistance. Some of the most common include:
- Strain Gauges: These sensors change resistance in response to mechanical stress, making them ideal for measuring deformation or strain in structural components.
- Temperature Sensors: Certain temperature-sensitive resistors, such as thermistors, can be used to measure electrical resistance based on changes in temperature.
- Pressure Sensors: Some pressure sensors utilize changes in resistance to measure variations in pressure.
- Photoresistors: These sensors change resistance based on the intensity of light hitting them, allowing for measurements related to ambient light levels.
Principles of Operation
The principles behind sensor-based resistance measurements vary depending on the type of sensor being used. However, most sensors operate based on the concept of changing resistance in response to a specific stimulus, such as temperature, pressure, strain, or light.
For example, a strain gauge will exhibit higher resistance when subjected to mechanical stress, while a thermistor will experience changes in resistance based on temperature fluctuations. By measuring these changes in resistance, engineers can derive valuable information about the environment or the object being monitored.
Steps for Measuring Resistance Using Sensors
When utilizing sensors to measure electrical resistance, certain steps must be followed to ensure accurate and reliable results. The following are the general steps involved in measuring resistance using sensors:
- Choose the appropriate sensor for the desired application based on the type of resistance being measured (e.g., strain, temperature, pressure, light).
- Calibrate the sensor to establish a baseline resistance measurement under normal conditions.
- Apply the sensor to the object or environment being monitored, ensuring proper connection and placement.
- Initiate the measurement process and record the resistance readings provided by the sensor.
- Analyze the data obtained from the sensor to draw conclusions about the electrical resistance in the system.
Conclusion
Using sensors to measure electrical resistance offers a convenient and efficient method for monitoring various parameters in electronic systems. By understanding the types of sensors available, the principles of their operation, and the steps involved in utilizing them, engineers can effectively measure resistance and diagnose issues within circuits.
Whether you are working on a complex electronic project or simply troubleshooting a faulty connection, employing sensors for resistance measurements can streamline your process and provide valuable insights into the behavior of electrical systems.