How to Measure Current Draw in a Power Circuit
Measuring current draw in a power circuit is essential for ensuring the efficiency and safety of your electrical system. Whether you are working with a simple appliance or a complex industrial machine, knowing how much current is flowing through the circuit can help you diagnose problems, optimize performance, and prevent overloading.
There are several methods to measure current draw in a power circuit, each with its own advantages and limitations. In this article, we will discuss some of the most common techniques and provide helpful tips for accurate measurements.
1. Use a Multimeter
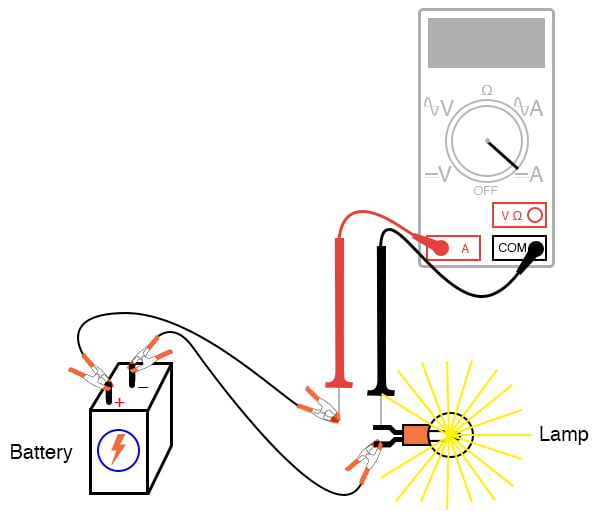
A multimeter is a versatile tool that can measure various electrical parameters, including current. To measure current draw in a power circuit using a multimeter, you will need to set it to the current measurement mode and then connect it in series with the circuit.
When using a multimeter to measure current draw, it is important to ensure that the meter’s current rating is higher than the expected current in the circuit. Otherwise, the meter could be damaged or provide inaccurate readings.
2. Use a Clamp Meter
A clamp meter is a convenient tool for measuring current draw in a power circuit without the need to break the circuit. Simply clamp the meter around the wire carrying the current, and it will display the current reading.
Clamp meters are especially useful for measuring current in large conductors or cables where it is impractical to disconnect the circuit for measurement. They are also safer to use in high-voltage environments compared to multimeters.
3. Use a Shunt Resistor
A shunt resistor is a precision resistor that is inserted in series with the circuit to measure the current flowing through it. By measuring the voltage drop across the resistor, you can calculate the current draw using Ohm’s Law (I = V/R).
Shunt resistors are commonly used in industrial applications where precise current measurements are required. They can handle high currents and are less affected by temperature variations compared to other methods.
4. Use a Current Probe
A current probe is a non-contact method for measuring current draw in a power circuit. Simply clamp the probe around the wire carrying the current, and it will provide an accurate reading without the need for direct contact.
Current probes are ideal for measuring current in live circuits where it is unsafe to make physical connections. They are also useful for troubleshooting intermittent current spikes or transients in the circuit.
5. Use a Power Analyzer
A power analyzer is a sophisticated tool that can measure not only current draw but also voltage, power factor, and other electrical parameters in a power circuit. Power analyzers are commonly used in industrial and commercial settings to monitor and optimize power usage.
Power analyzers provide detailed insights into the power quality and efficiency of a circuit, making them invaluable for energy audits, power management, and equipment testing. They can also help identify power quality issues such as harmonics or voltage fluctuations.
Conclusion
Measuring current draw in a power circuit is crucial for maintaining the performance and safety of electrical systems. Whether you choose to use a multimeter, clamp meter, shunt resistor, current probe, or power analyzer, it is important to select the right tool for the job and follow proper safety precautions.
By accurately measuring current draw, you can diagnose faults, optimize energy usage, and prevent costly downtime. So, don’t overlook the importance of current measurements in your electrical system!
How to Measure Current Draw in a Power Circuit
Measuring current draw in a power circuit is essential for ensuring the efficiency and safety of your electrical system. Whether you are working with a simple appliance or a complex industrial machine, knowing how much current is flowing through the circuit can help you diagnose problems, optimize performance, and prevent overloading.
There are several methods to measure current draw in a power circuit, each with its own advantages and limitations. In this article, we will discuss some of the most common techniques and provide helpful tips for accurate measurements.
1. Use a Multimeter
A multimeter is a versatile tool that can measure various electrical parameters, including current. To measure current draw in a power circuit using a multimeter, you will need to set it to the current measurement mode and then connect it in series with the circuit.
When using a multimeter to measure current draw, it is important to ensure that the meter’s current rating is higher than the expected current in the circuit. Otherwise, the meter could be damaged or provide inaccurate readings.
2. Use a Clamp Meter
A clamp meter is a convenient tool for measuring current draw in a power circuit without the need to break the circuit. Simply clamp the meter around the wire carrying the current, and it will display the current reading.
Clamp meters are especially useful for measuring current in large conductors or cables where it is impractical to disconnect the circuit for measurement. They are also safer to use in high-voltage environments compared to multimeters.
3. Use a Shunt Resistor
A shunt resistor is a precision resistor that is inserted in series with the circuit to measure the current flowing through it. By measuring the voltage drop across the resistor, you can calculate the current draw using Ohm’s Law (I = V/R).
Shunt resistors are commonly used in industrial applications where precise current measurements are required. They can handle high currents and are less affected by temperature variations compared to other methods.
4. Use a Current Probe
A current probe is a non-contact method for measuring current draw in a power circuit. Simply clamp the probe around the wire carrying the current, and it will provide an accurate reading without the need for direct contact.
Current probes are ideal for measuring current in live circuits where it is unsafe to make physical connections. They are also useful for troubleshooting intermittent current spikes or transients in the circuit.
5. Use a Power Analyzer
A power analyzer is a sophisticated tool that can measure not only current draw but also voltage, power factor, and other electrical parameters in a power circuit. Power analyzers are commonly used in industrial and commercial settings to monitor and optimize power usage.
Power analyzers provide detailed insights into the power quality and efficiency of a circuit, making them invaluable for energy audits, power management, and equipment testing. They can also help identify power quality issues such as harmonics or voltage fluctuations.
Conclusion
Measuring current draw in a power circuit is crucial for maintaining the performance and safety of electrical systems. Whether you choose to use a multimeter, clamp meter, shunt resistor, current probe, or power analyzer, it is important to select the right tool for the job and follow proper safety precautions.
By accurately measuring current draw, you can diagnose faults, optimize energy usage, and prevent costly downtime. So, don’t overlook the importance of current measurements in your electrical system!