How to Interface a PM2.5 Dust Sensor
PM2.5 dust sensors are valuable tools for monitoring air quality and detecting fine particulate matter. These sensors are commonly used in a variety of applications, from indoor air quality monitoring to industrial pollution control. If you are looking to interface a PM2.5 dust sensor with your project or device, this guide will help you get started.
There are several different types of PM2.5 dust sensors available on the market, but they all operate on similar principles. These sensors use a laser or LED light source to detect particles in the air, and then measure the scattering or absorption of light to determine the concentration of particulate matter.
Choosing the Right Sensor
Before you can interface a PM2.5 dust sensor, you need to choose the right sensor for your application. Consider factors such as the sensor’s measurement range, accuracy, and sensitivity, as well as its physical size and power requirements. Some sensors may also offer additional features, such as the ability to detect different types of particles or to communicate via a specific protocol.
Once you have selected the appropriate sensor for your project, you will need to familiarize yourself with the sensor’s datasheet and documentation. This information will provide you with important details about the sensor’s specifications, pinout, and operating principles, which will be essential for interfacing the sensor correctly.
Interfacing the Sensor
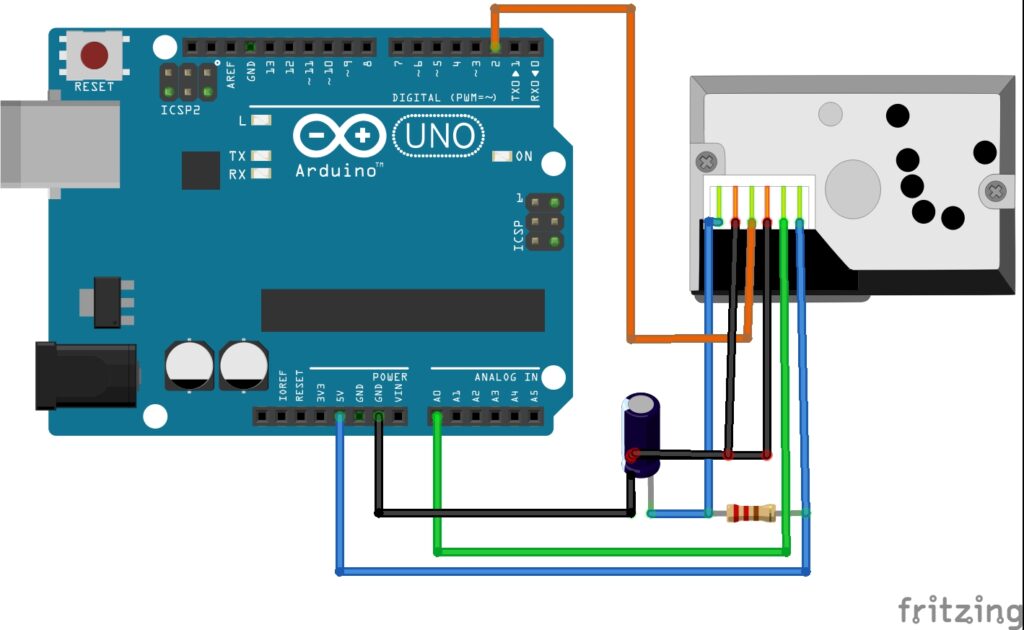
To interface a PM2.5 dust sensor with your project, you will typically need to connect the sensor to a microcontroller or single-board computer. Most sensors communicate using a standard protocol such as UART, I2C, or SPI, so you will need to ensure that your chosen microcontroller or SBC supports the same protocol.
Start by connecting the sensor’s power and ground pins to the corresponding pins on your microcontroller or SBC. Then, connect the sensor’s data pins to the appropriate communication pins on your device. Follow the sensor’s datasheet to determine the correct pinout and connections for your specific sensor model.
Once the sensor is properly connected, you can begin interfacing with it using the appropriate software libraries and code. Many sensor manufacturers provide libraries and example code to help you get started, so be sure to check their website or documentation for guidance on how to communicate with the sensor.
Calibrating the Sensor
After you have successfully interfaced the sensor with your project, you may need to calibrate the sensor to ensure accurate and reliable measurements. Calibration is typically done by exposing the sensor to known concentrations of particulate matter and adjusting the sensor’s settings or code to match the expected readings.
Follow the calibration procedures outlined in the sensor’s datasheet or documentation, and be sure to test the sensor’s accuracy and precision under various conditions. Calibration is an important step in using a PM2.5 dust sensor effectively, so take the time to calibrate your sensor properly.
Conclusion
Interfacing a PM2.5 dust sensor with your project can be a valuable way to monitor air quality and detect particulate matter in the environment. By choosing the right sensor, interfacing it correctly, and calibrating it effectively, you can ensure that your sensor provides accurate and reliable measurements for your application.
How to Interface a PM2.5 Dust Sensor
PM2.5 dust sensors are valuable tools for monitoring air quality and detecting fine particulate matter. These sensors are commonly used in a variety of applications, from indoor air quality monitoring to industrial pollution control. If you are looking to interface a PM2.5 dust sensor with your project or device, this guide will help you get started.
There are several different types of PM2.5 dust sensors available on the market, but they all operate on similar principles. These sensors use a laser or LED light source to detect particles in the air, and then measure the scattering or absorption of light to determine the concentration of particulate matter.
Choosing the Right Sensor
Before you can interface a PM2.5 dust sensor, you need to choose the right sensor for your application. Consider factors such as the sensor’s measurement range, accuracy, and sensitivity, as well as its physical size and power requirements. Some sensors may also offer additional features, such as the ability to detect different types of particles or to communicate via a specific protocol.
Once you have selected the appropriate sensor for your project, you will need to familiarize yourself with the sensor’s datasheet and documentation. This information will provide you with important details about the sensor’s specifications, pinout, and operating principles, which will be essential for interfacing the sensor correctly.
Interfacing the Sensor
To interface a PM2.5 dust sensor with your project, you will typically need to connect the sensor to a microcontroller or single-board computer. Most sensors communicate using a standard protocol such as UART, I2C, or SPI, so you will need to ensure that your chosen microcontroller or SBC supports the same protocol.
Start by connecting the sensor’s power and ground pins to the corresponding pins on your microcontroller or SBC. Then, connect the sensor’s data pins to the appropriate communication pins on your device. Follow the sensor’s datasheet to determine the correct pinout and connections for your specific sensor model.
Once the sensor is properly connected, you can begin interfacing with it using the appropriate software libraries and code. Many sensor manufacturers provide libraries and example code to help you get started, so be sure to check their website or documentation for guidance on how to communicate with the sensor.
Calibrating the Sensor
After you have successfully interfaced the sensor with your project, you may need to calibrate the sensor to ensure accurate and reliable measurements. Calibration is typically done by exposing the sensor to known concentrations of particulate matter and adjusting the sensor’s settings or code to match the expected readings.
Follow the calibration procedures outlined in the sensor’s datasheet or documentation, and be sure to test the sensor’s accuracy and precision under various conditions. Calibration is an important step in using a PM2.5 dust sensor effectively, so take the time to calibrate your sensor properly.
Conclusion
Interfacing a PM2.5 dust sensor with your project can be a valuable way to monitor air quality and detect particulate matter in the environment. By choosing the right sensor, interfacing it correctly, and calibrating it effectively, you can ensure that your sensor provides accurate and reliable measurements for your application.