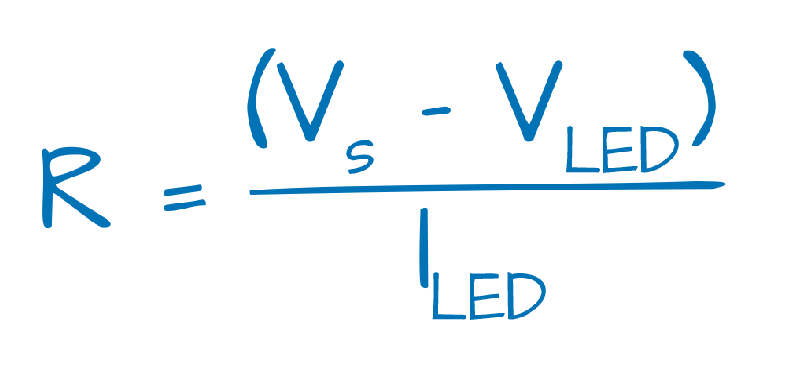How to Calculate Resistor Value for LEDs
LEDs, or Light Emitting Diodes, are popular components used in various electronic devices and circuits due to their energy efficiency and long lifespan. When incorporating LEDs into a circuit, it is essential to calculate the appropriate resistor value to ensure proper operation and prevent damage to the LEDs. In this article, we will guide you through the process of determining the resistor value for LEDs in your circuit.
Understanding LED Voltage and Current Ratings
Before calculating the resistor value for LEDs, it is crucial to understand the voltage and current ratings of the LED you are working with. LEDs typically have a forward voltage rating (Vf) and a forward current rating (If), which indicate the minimum voltage and current required for the LED to turn on and operate correctly.
For example, let’s say you have an LED with a forward voltage rating of 2.2V and a forward current rating of 20mA. These values are essential for calculating the appropriate resistor value to limit the current flowing through the LED and prevent it from being damaged.
Calculating Resistor Value Using Ohm’s Law
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental principle in electronics that relates voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R). The formula for Ohm’s Law is as follows:
V = I * R
Where:
- V is the voltage across the resistor (in volts)
- I is the current flowing through the resistor (in amperes)
- R is the resistance value of the resistor (in ohms)
To calculate the resistor value for an LED circuit, you can rearrange the equation to solve for the resistance:
R = (Vsource - Vf) / If
Where:
- Vsource is the source voltage supplying the LED circuit
- Vf is the forward voltage rating of the LED
- If is the forward current rating of the LED
Using the example of an LED with a Vf of 2.2V and an If of 20mA, let’s say you are using a 5V power supply. To calculate the resistor value, you would plug in the values into the formula:
R = (5V – 2.2V) / 0.02A = 140 ohms
Therefore, in this case, you would need a 140 ohm resistor to limit the current flowing through the LED to 20mA when powered by a 5V source.
Choosing the Closest Standard Resistor Value
Once you have calculated the resistor value using Ohm’s Law, it is essential to choose the closest standard resistor value that is equal to or higher than the calculated value. Resistor values come in standard increments, so you may need to select the next highest value to ensure proper current limiting and LED performance.
For example, if you calculated a resistor value of 140 ohms, you would likely choose a 150 ohm standard resistor to ensure the LED operates within its specified current rating.
Conclusion
Calculating the resistor value for LEDs is a crucial step in designing LED circuits to ensure proper current limiting and prevent damage to the LEDs. By understanding the voltage and current ratings of the LED, applying Ohm’s Law, and selecting the appropriate resistor value, you can create efficient and reliable LED circuits for your electronic projects.
Experiment with different resistor values and LED configurations to optimize your circuit design and achieve the desired lighting effects. Remember to always double-check your calculations and test your circuit to verify its performance before finalizing your project.
How to Calculate Resistor Value for LEDs
LEDs, or Light Emitting Diodes, are popular components used in various electronic devices and circuits due to their energy efficiency and long lifespan. When incorporating LEDs into a circuit, it is essential to calculate the appropriate resistor value to ensure proper operation and prevent damage to the LEDs. In this article, we will guide you through the process of determining the resistor value for LEDs in your circuit.
Understanding LED Voltage and Current Ratings
Before calculating the resistor value for LEDs, it is crucial to understand the voltage and current ratings of the LED you are working with. LEDs typically have a forward voltage rating (Vf) and a forward current rating (If), which indicate the minimum voltage and current required for the LED to turn on and operate correctly.
For example, let’s say you have an LED with a forward voltage rating of 2.2V and a forward current rating of 20mA. These values are essential for calculating the appropriate resistor value to limit the current flowing through the LED and prevent it from being damaged.
Calculating Resistor Value Using Ohm’s Law
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental principle in electronics that relates voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R). The formula for Ohm’s Law is as follows:
V = I * R
Where:
- V is the voltage across the resistor (in volts)
- I is the current flowing through the resistor (in amperes)
- R is the resistance value of the resistor (in ohms)
To calculate the resistor value for an LED circuit, you can rearrange the equation to solve for the resistance:
R = (Vsource - Vf) / If
Where:
- Vsource is the source voltage supplying the LED circuit
- Vf is the forward voltage rating of the LED
- If is the forward current rating of the LED
Using the example of an LED with a Vf of 2.2V and an If of 20mA, let’s say you are using a 5V power supply. To calculate the resistor value, you would plug in the values into the formula:
R = (5V – 2.2V) / 0.02A = 140 ohms
Therefore, in this case, you would need a 140 ohm resistor to limit the current flowing through the LED to 20mA when powered by a 5V source.
Choosing the Closest Standard Resistor Value
Once you have calculated the resistor value using Ohm’s Law, it is essential to choose the closest standard resistor value that is equal to or higher than the calculated value. Resistor values come in standard increments, so you may need to select the next highest value to ensure proper current limiting and LED performance.
For example, if you calculated a resistor value of 140 ohms, you would likely choose a 150 ohm standard resistor to ensure the LED operates within its specified current rating.
Conclusion
Calculating the resistor value for LEDs is a crucial step in designing LED circuits to ensure proper current limiting and prevent damage to the LEDs. By understanding the voltage and current ratings of the LED, applying Ohm’s Law, and selecting the appropriate resistor value, you can create efficient and reliable LED circuits for your electronic projects.
Experiment with different resistor values and LED configurations to optimize your circuit design and achieve the desired lighting effects. Remember to always double-check your calculations and test your circuit to verify its performance before finalizing your project.