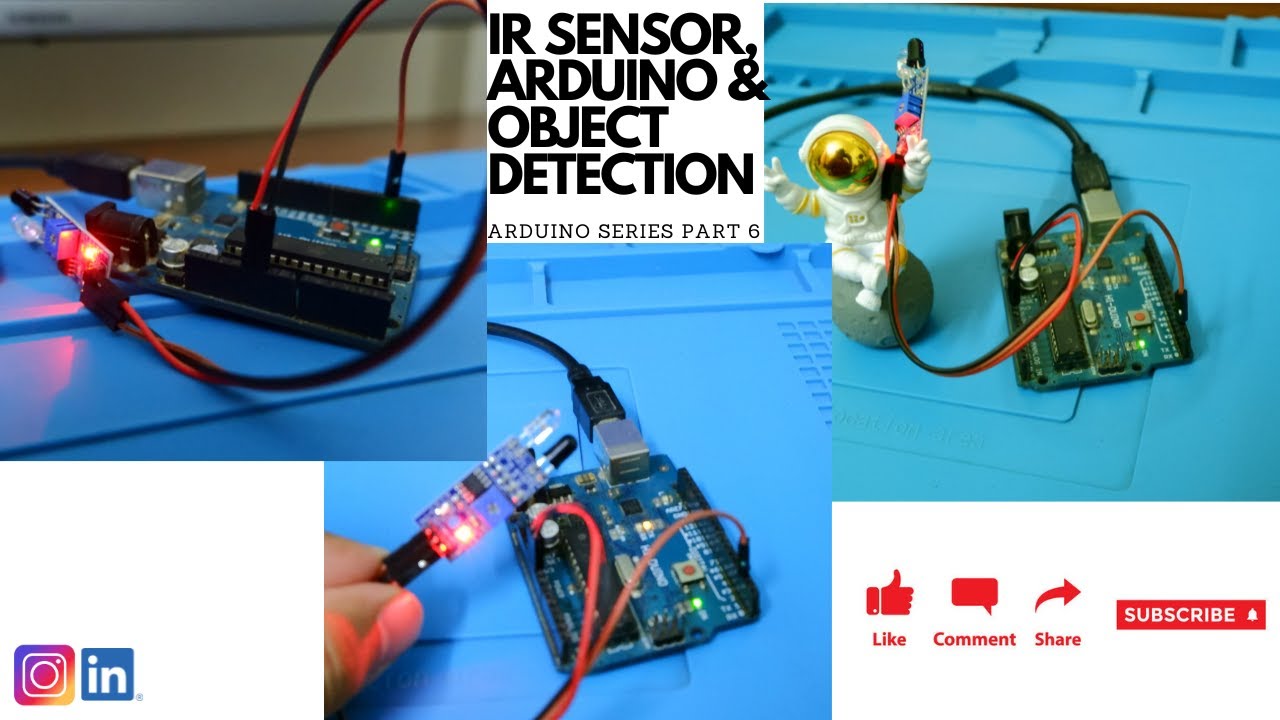
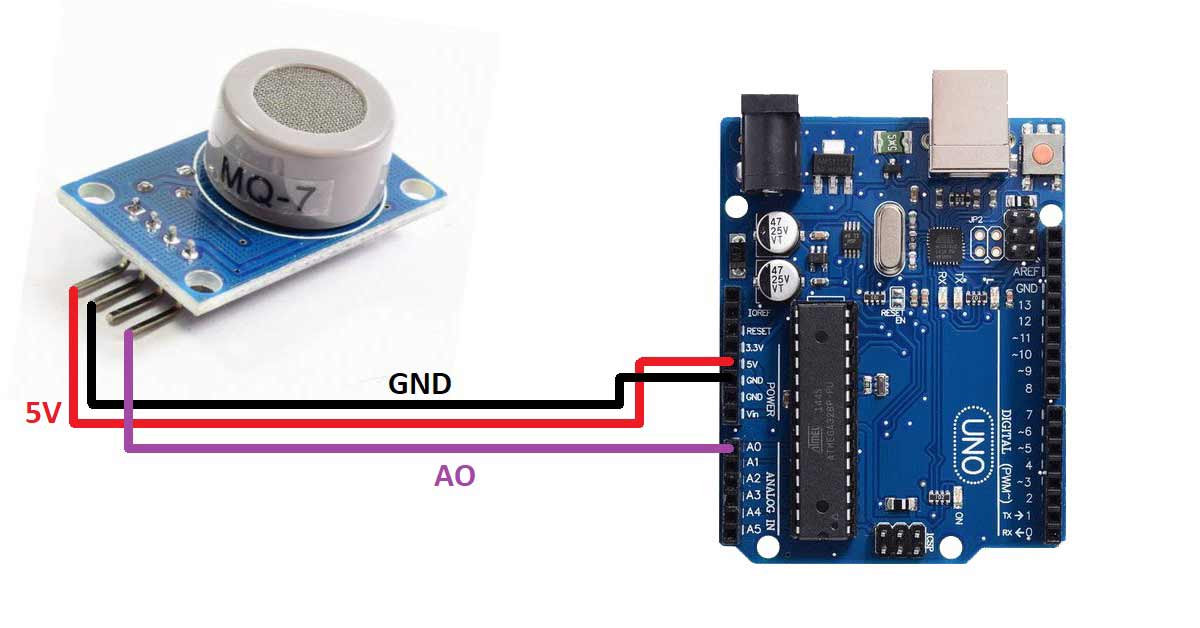
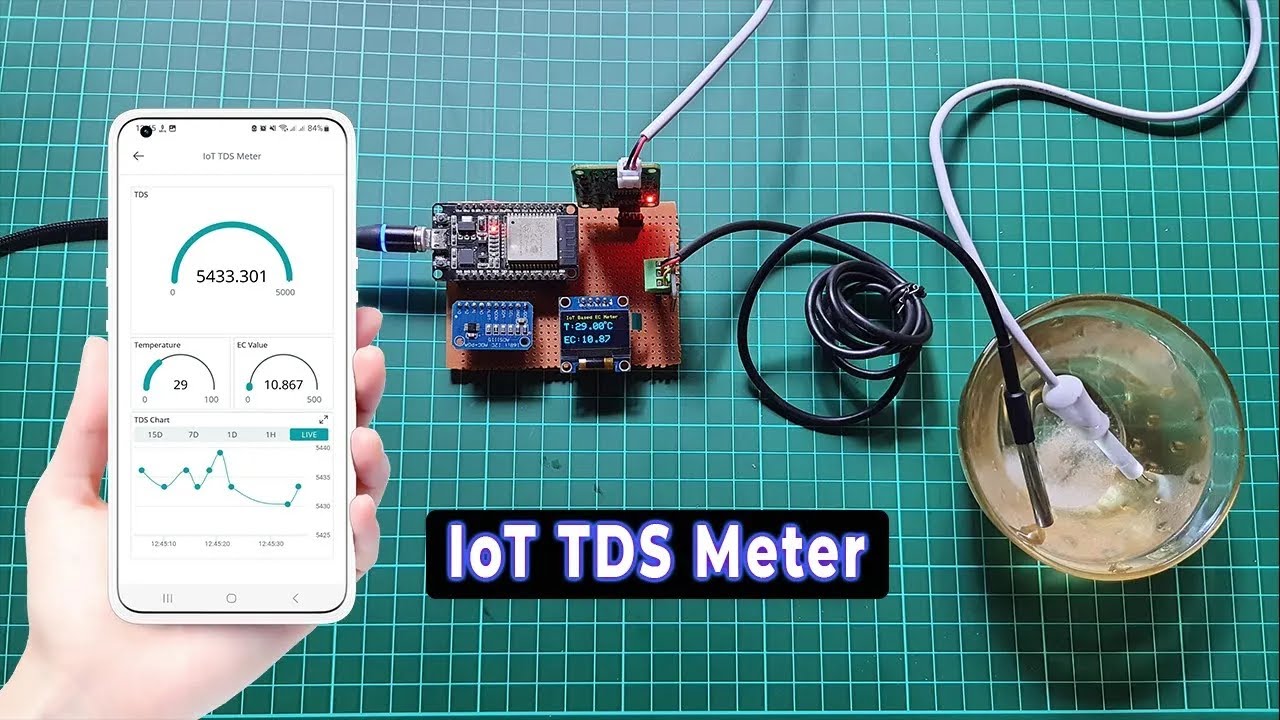
How to Use a Rotary Encoder for Angle Measurement
Rotary encoders are widely used in various applications for measuring rotational position and speed. In this article, we will discuss how to use a rotary encoder specifically for angle measurement. By the end of this guide, you will have a good understanding of how to implement a rotary encoder for accurate angle measurement.
What is a Rotary Encoder?
A rotary encoder is an electro-mechanical device that converts the angular position or motion of a shaft into an analog or digital signal. It is commonly used in robotics, CNC machines, computer peripherals, and other industrial applications for precise angle measurement. Unlike a potentiometer, a rotary encoder can rotate indefinitely without mechanical stops.
Types of Rotary Encoders
There are two main types of rotary encoders: incremental and absolute. Incremental encoders generate a series of pulse outputs as the shaft rotates, while absolute encoders provide a unique digital code for each shaft position. For angle measurement, an absolute encoder is generally preferred for its precise angular resolution.
How to Connect a Rotary Encoder
Connecting a rotary encoder is relatively straightforward. Most rotary encoders come with three output pins: ground, power, and signal. You can connect the ground pin to the ground of your system, the power pin to the supply voltage, and the signal pin to the input of a microcontroller or a dedicated encoder interface IC.
Programming a Rotary Encoder
Once you have connected the rotary encoder to your system, you will need to program the microcontroller or encoder interface IC to read the encoder signals. Depending on the type of encoder you are using, you may need to configure the software to handle the pulse outputs (for incremental encoders) or the digital codes (for absolute encoders).
Calibrating the Rotary Encoder
Before using the rotary encoder for angle measurement, it is essential to calibrate the encoder to ensure accurate readings. You can calibrate the encoder by rotating the shaft to known reference angles and comparing the readings with the expected values. This calibration process will help you account for any offset or noise in the encoder signals.
Reading Angle Measurements
Once the rotary encoder is connected, programmed, and calibrated, you can start reading angle measurements from the encoder. Depending on the resolution of the encoder and the application requirements, you can convert the encoder signals into angular units such as degrees, radians, or revolutions.
Applications of Rotary Encoders
Rotary encoders have a wide range of applications, including robotics, industrial automation, CNC machining, and motion control systems. By accurately measuring angles, rotary encoders play a crucial role in monitoring and controlling the rotational motion of various mechanical systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, rotary encoders are versatile devices that can be used for precise angle measurement in a variety of applications. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can effectively use a rotary encoder to measure angles with accuracy and reliability. Whether you are working on a robotics project or a CNC machine, a rotary encoder is a valuable tool for rotational position sensing.
How to Use a Rotary Encoder for Angle Measurement
Rotary encoders are widely used in various applications for measuring rotational position and speed. In this article, we will discuss how to use a rotary encoder specifically for angle measurement. By the end of this guide, you will have a good understanding of how to implement a rotary encoder for accurate angle measurement.
What is a Rotary Encoder?
A rotary encoder is an electro-mechanical device that converts the angular position or motion of a shaft into an analog or digital signal. It is commonly used in robotics, CNC machines, computer peripherals, and other industrial applications for precise angle measurement. Unlike a potentiometer, a rotary encoder can rotate indefinitely without mechanical stops.
Types of Rotary Encoders
There are two main types of rotary encoders: incremental and absolute. Incremental encoders generate a series of pulse outputs as the shaft rotates, while absolute encoders provide a unique digital code for each shaft position. For angle measurement, an absolute encoder is generally preferred for its precise angular resolution.
How to Connect a Rotary Encoder
Connecting a rotary encoder is relatively straightforward. Most rotary encoders come with three output pins: ground, power, and signal. You can connect the ground pin to the ground of your system, the power pin to the supply voltage, and the signal pin to the input of a microcontroller or a dedicated encoder interface IC.
Programming a Rotary Encoder
Once you have connected the rotary encoder to your system, you will need to program the microcontroller or encoder interface IC to read the encoder signals. Depending on the type of encoder you are using, you may need to configure the software to handle the pulse outputs (for incremental encoders) or the digital codes (for absolute encoders).
Calibrating the Rotary Encoder
Before using the rotary encoder for angle measurement, it is essential to calibrate the encoder to ensure accurate readings. You can calibrate the encoder by rotating the shaft to known reference angles and comparing the readings with the expected values. This calibration process will help you account for any offset or noise in the encoder signals.
Reading Angle Measurements
Once the rotary encoder is connected, programmed, and calibrated, you can start reading angle measurements from the encoder. Depending on the resolution of the encoder and the application requirements, you can convert the encoder signals into angular units such as degrees, radians, or revolutions.
Applications of Rotary Encoders
Rotary encoders have a wide range of applications, including robotics, industrial automation, CNC machining, and motion control systems. By accurately measuring angles, rotary encoders play a crucial role in monitoring and controlling the rotational motion of various mechanical systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, rotary encoders are versatile devices that can be used for precise angle measurement in a variety of applications. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can effectively use a rotary encoder to measure angles with accuracy and reliability. Whether you are working on a robotics project or a CNC machine, a rotary encoder is a valuable tool for rotational position sensing.