How to Design a Power-Efficient Wireless Sensor
Wireless sensors are essential components in various industries, allowing for remote monitoring and data collection. However, one of the significant challenges with wireless sensors is ensuring they are power-efficient. A power-efficient wireless sensor can prolong its battery life, reduce maintenance costs, and overall improve the device’s performance. In this article, we will explore some tips on how to design a power-efficient wireless sensor.
1. Choose the Right Components
When designing a wireless sensor, selecting the right components is crucial for energy efficiency. Opt for low-power components that consume minimal energy during operation. Components such as microcontrollers, transceivers, and sensors should be carefully chosen to ensure they meet the power requirements of the sensor while maintaining optimal performance.
2. Implement Low-Power Protocols
Utilizing low-power protocols such as Zigbee, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), or LoRa can help reduce energy consumption in wireless sensors. These protocols are designed to minimize power usage during data transmission, enabling the sensor to operate efficiently while maximizing battery life.
3. Optimize Data Transmission
Efficient data transmission is essential for power-saving in wireless sensors. Implementing techniques such as data aggregation, data compression, and duty cycling can reduce the amount of data sent over the network, consequently reducing power consumption. By optimizing data transmission, the sensor can conserve energy and operate more efficiently.
4. Use Power Management Techniques
Implementing power management techniques such as sleep modes, dynamic voltage scaling, and power gating can significantly improve the energy efficiency of wireless sensors. By putting the sensor into low-power modes when not in use or reducing voltage during idle times, power consumption can be minimized, extending the battery life of the sensor.
5. Conduct Energy Profiling
Conducting energy profiling is essential to identify energy-intensive operations within the wireless sensor. By analyzing energy consumption at various stages of operation, designers can optimize the sensor’s performance and prioritize energy-saving measures. Energy profiling enables designers to understand where energy is being consumed and implement targeted solutions for power efficiency.
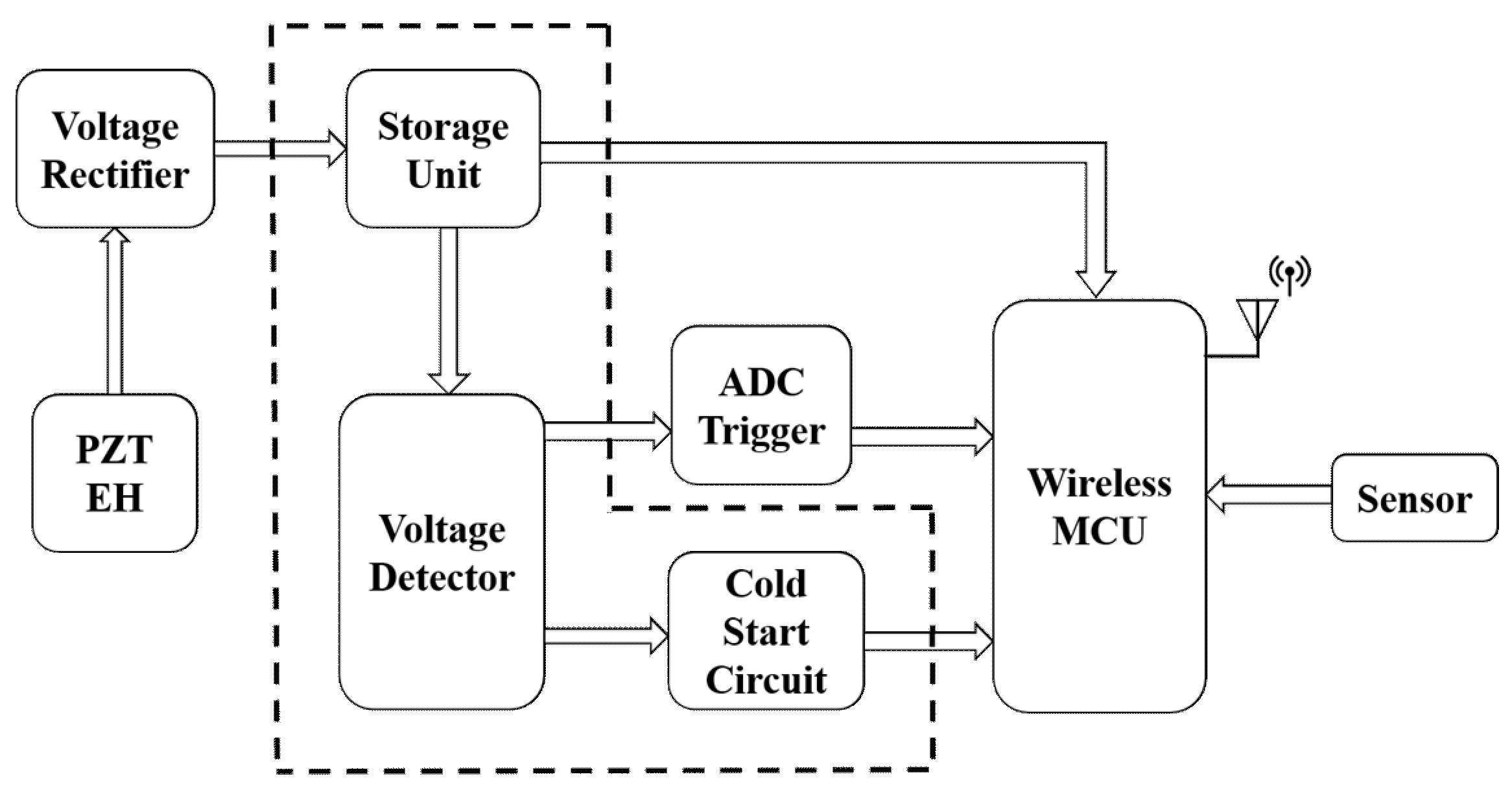
6. Consider Energy Harvesting
Energy harvesting is a sustainable solution to power wireless sensors without relying solely on batteries. By utilizing solar panels, kinetic energy, or thermoelectric generators, sensors can generate electricity from the surrounding environment, reducing the need for frequent battery replacements. Integrating energy harvesting technologies can make wireless sensors more sustainable and reduce long-term costs.
Conclusion
Designing a power-efficient wireless sensor requires a combination of careful component selection, protocol optimization, data transmission techniques, power management strategies, energy profiling, and consideration for energy harvesting. By implementing these tips and techniques, designers can create wireless sensors that are not only energy-efficient but also reliable and cost-effective. With the increasing demand for wireless sensor applications, prioritizing power efficiency is essential to meet industry needs and ensure long-term success.
Was this helpful?
0 / 0