Best Power Supply for Arduino Projects
When it comes to powering your Arduino projects, having a reliable and stable power supply is essential. Whether you are working on a simple LED project or a complex robotics project, choosing the right power supply can make a huge difference in the performance and longevity of your project.
In this article, we will take a look at some of the best power supply options for Arduino projects. From battery packs to wall adapters, we will explore the pros and cons of each type of power supply to help you make an informed decision for your next project.
1. USB Power Bank
One of the most convenient and portable power supply options for Arduino projects is a USB power bank. These power banks are typically used to charge smartphones and other devices, but they can also be used to power Arduino projects via the USB port.
USB power banks come in various capacities, ranging from a few thousand milliampere-hours (mAh) to tens of thousands of mAh. This makes them suitable for powering a wide range of Arduino projects, from simple sensors to more power-hungry devices.
One of the main advantages of using a USB power bank is its portability. You can easily carry it around with you and power your Arduino projects on the go. Additionally, many USB power banks come with multiple USB ports, allowing you to power multiple Arduino boards simultaneously.
However, one drawback of using a USB power bank is its limited output current. Most USB power banks are designed to deliver up to 2.4 amps of current, which may not be enough for some power-hungry Arduino projects. It is important to check the current requirements of your project before using a USB power bank as a power supply.
2. AC/DC Adapter
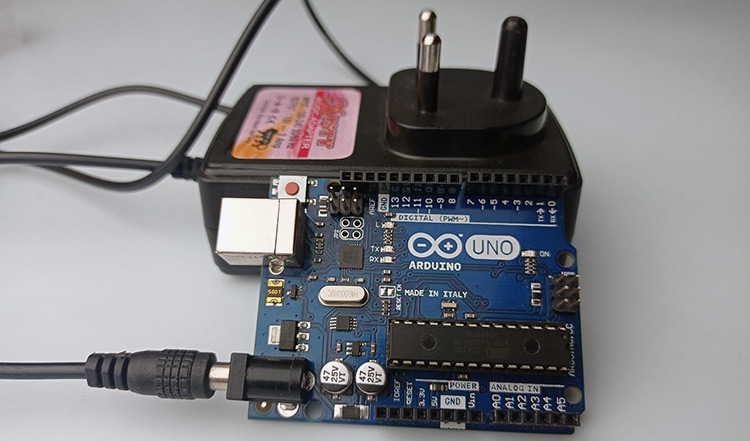
Another popular power supply option for Arduino projects is an AC/DC adapter. These adapters are commonly used to power electronic devices such as laptops, routers, and printers, but they can also be used to power Arduino projects.
AC/DC adapters come in various voltage and current ratings, making them suitable for a wide range of Arduino projects. They typically provide a stable and reliable power supply, which is essential for projects that require precise voltage levels.
One advantage of using an AC/DC adapter is its high output current capability. Most AC/DC adapters can deliver up to several amps of current, which is more than enough for most Arduino projects. This makes them ideal for powering projects that require high current levels, such as motor controllers and LED displays.
However, one drawback of using an AC/DC adapter is its lack of portability. These adapters are usually bulky and require an outlet to operate, which may limit where you can use them to power your Arduino projects.
3. LiPo Battery
For Arduino projects that require a portable power supply, a LiPo (Lithium Polymer) battery is an excellent option. LiPo batteries are lightweight and compact, making them ideal for powering projects that need to be mobile or wearable.
LiPo batteries come in various capacities and voltages, allowing you to select the right battery for your project’s power requirements. They also have a high energy density, which means they can deliver a lot of power in a small and lightweight package.
One advantage of using a LiPo battery is its rechargeable nature. You can easily recharge a LiPo battery using a dedicated charger, making it a cost-effective power supply option in the long run. Additionally, many LiPo batteries come with built-in protection circuitry to prevent overcharging and over-discharging, ensuring the safety of your project.
However, one drawback of using a LiPo battery is its voltage limitations. Most LiPo batteries provide a nominal voltage of 3.7 volts, which may not be suitable for projects that require higher voltages. You may need to use a voltage regulator or boost converter to adjust the voltage to match your project’s requirements.
4. Solar Panel
For Arduino projects that need to be powered off-grid or in remote locations, a solar panel is a sustainable and eco-friendly power supply option. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, allowing you to power your projects using renewable energy.
Solar panels come in various sizes and wattages, allowing you to select the right panel for your project’s power requirements. They can be used to directly power your Arduino projects or charge a battery pack for continuous power supply, depending on your project’s needs.
One advantage of using a solar panel is its sustainability. By harnessing the power of the sun, you can power your Arduino projects without relying on traditional energy sources. This not only reduces your carbon footprint but also allows you to operate your projects in remote locations where power outlets may not be readily available.
However, one drawback of using a solar panel is its dependency on sunlight. If you are working on a project that requires constant power supply, a solar panel may not be the most reliable option, especially during periods of low sunlight or bad weather.
Conclusion
When it comes to powering your Arduino projects, the right power supply can make all the difference in the performance and reliability of your project. Whether you choose a USB power bank for its portability, an AC/DC adapter for its high output current capability, a LiPo battery for its rechargeable nature, or a solar panel for its sustainability, each power supply option has its own advantages and considerations.
It is important to carefully consider your project’s power requirements and choose the power supply that best fits your needs. By selecting the right power supply, you can ensure that your Arduino projects run smoothly and efficiently, bringing your ideas to life with power and precision.
Best Power Supply for Arduino Projects
When it comes to powering your Arduino projects, having a reliable and stable power supply is essential. Whether you are working on a simple LED project or a complex robotics project, choosing the right power supply can make a huge difference in the performance and longevity of your project.
In this article, we will take a look at some of the best power supply options for Arduino projects. From battery packs to wall adapters, we will explore the pros and cons of each type of power supply to help you make an informed decision for your next project.
1. USB Power Bank
One of the most convenient and portable power supply options for Arduino projects is a USB power bank. These power banks are typically used to charge smartphones and other devices, but they can also be used to power Arduino projects via the USB port.
USB power banks come in various capacities, ranging from a few thousand milliampere-hours (mAh) to tens of thousands of mAh. This makes them suitable for powering a wide range of Arduino projects, from simple sensors to more power-hungry devices.
One of the main advantages of using a USB power bank is its portability. You can easily carry it around with you and power your Arduino projects on the go. Additionally, many USB power banks come with multiple USB ports, allowing you to power multiple Arduino boards simultaneously.
However, one drawback of using a USB power bank is its limited output current. Most USB power banks are designed to deliver up to 2.4 amps of current, which may not be enough for some power-hungry Arduino projects. It is important to check the current requirements of your project before using a USB power bank as a power supply.
2. AC/DC Adapter
Another popular power supply option for Arduino projects is an AC/DC adapter. These adapters are commonly used to power electronic devices such as laptops, routers, and printers, but they can also be used to power Arduino projects.
AC/DC adapters come in various voltage and current ratings, making them suitable for a wide range of Arduino projects. They typically provide a stable and reliable power supply, which is essential for projects that require precise voltage levels.
One advantage of using an AC/DC adapter is its high output current capability. Most AC/DC adapters can deliver up to several amps of current, which is more than enough for most Arduino projects. This makes them ideal for powering projects that require high current levels, such as motor controllers and LED displays.
However, one drawback of using an AC/DC adapter is its lack of portability. These adapters are usually bulky and require an outlet to operate, which may limit where you can use them to power your Arduino projects.
3. LiPo Battery
For Arduino projects that require a portable power supply, a LiPo (Lithium Polymer) battery is an excellent option. LiPo batteries are lightweight and compact, making them ideal for powering projects that need to be mobile or wearable.
LiPo batteries come in various capacities and voltages, allowing you to select the right battery for your project’s power requirements. They also have a high energy density, which means they can deliver a lot of power in a small and lightweight package.
One advantage of using a LiPo battery is its rechargeable nature. You can easily recharge a LiPo battery using a dedicated charger, making it a cost-effective power supply option in the long run. Additionally, many LiPo batteries come with built-in protection circuitry to prevent overcharging and over-discharging, ensuring the safety of your project.
However, one drawback of using a LiPo battery is its voltage limitations. Most LiPo batteries provide a nominal voltage of 3.7 volts, which may not be suitable for projects that require higher voltages. You may need to use a voltage regulator or boost converter to adjust the voltage to match your project’s requirements.
4. Solar Panel
For Arduino projects that need to be powered off-grid or in remote locations, a solar panel is a sustainable and eco-friendly power supply option. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, allowing you to power your projects using renewable energy.
Solar panels come in various sizes and wattages, allowing you to select the right panel for your project’s power requirements. They can be used to directly power your Arduino projects or charge a battery pack for continuous power supply, depending on your project’s needs.
One advantage of using a solar panel is its sustainability. By harnessing the power of the sun, you can power your Arduino projects without relying on traditional energy sources. This not only reduces your carbon footprint but also allows you to operate your projects in remote locations where power outlets may not be readily available.
However, one drawback of using a solar panel is its dependency on sunlight. If you are working on a project that requires constant power supply, a solar panel may not be the most reliable option, especially during periods of low sunlight or bad weather.
Conclusion
When it comes to powering your Arduino projects, the right power supply can make all the difference in the performance and reliability of your project. Whether you choose a USB power bank for its portability, an AC/DC adapter for its high output current capability, a LiPo battery for its rechargeable nature, or a solar panel for its sustainability, each power supply option has its own advantages and considerations.
It is important to carefully consider your project’s power requirements and choose the power supply that best fits your needs. By selecting the right power supply, you can ensure that your Arduino projects run smoothly and efficiently, bringing your ideas to life with power and precision.