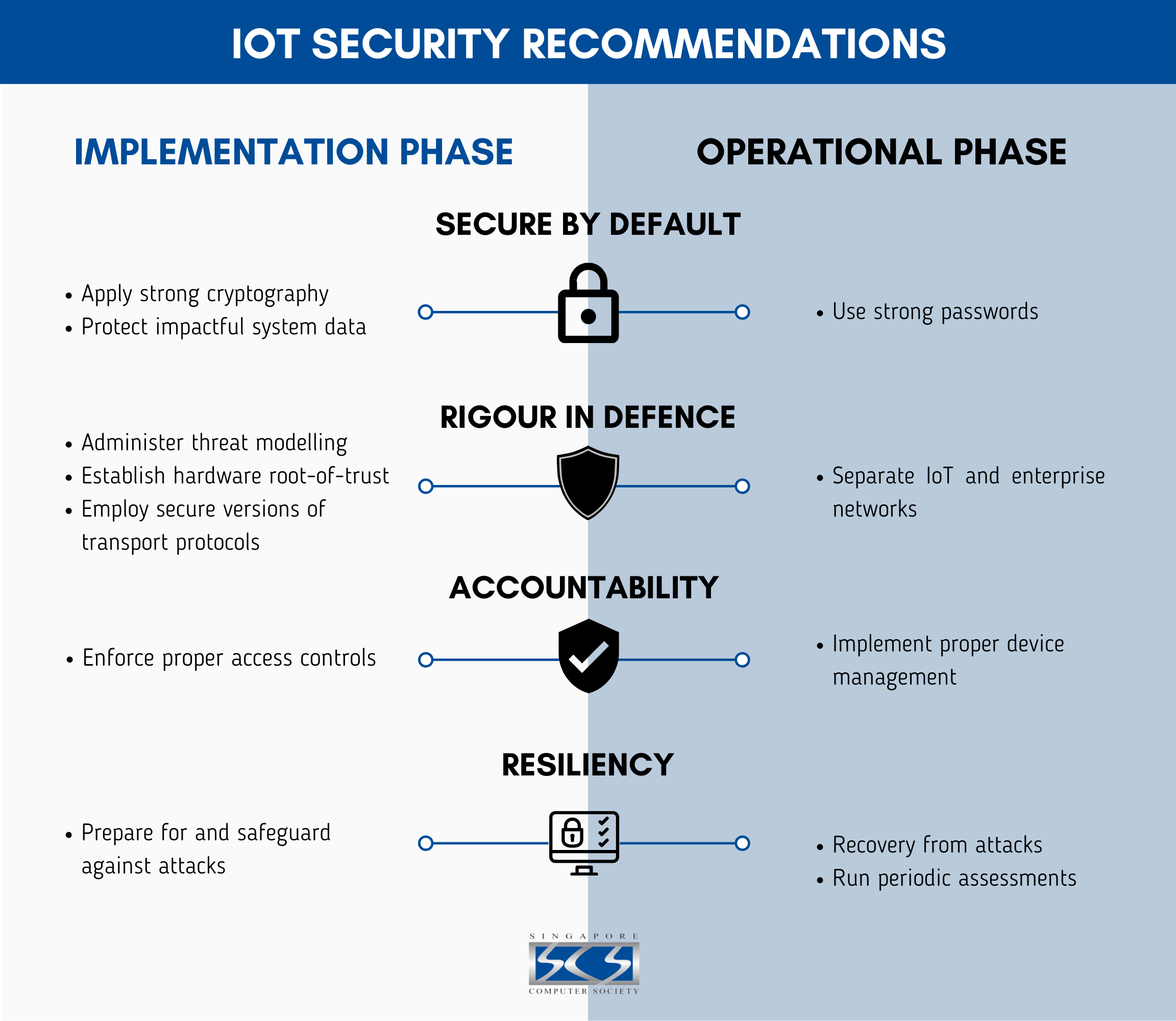
Best IoT Security Protocols
When it comes to the Internet of Things (IoT), security should always be a top priority. With the increasing number of connected devices in our homes and workplaces, it’s crucial to ensure that sensitive data and systems are protected from potential cyber threats. One of the best ways to secure IoT devices is by implementing strong security protocols. In this article, we will discuss some of the best IoT security protocols that can help safeguard your connected devices.
1. Transport Layer Security (TLS)
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a cryptographic protocol that provides secure communication over a computer network. It is commonly used to secure web browsing, email, and other internet applications. When it comes to IoT devices, TLS can help encrypt data as it is transmitted between devices and servers, preventing unauthorized access or tampering. Implementing TLS can help protect sensitive information and ensure the integrity of data exchanges.
2. Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS)
Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) is a variant of TLS that is specifically designed to secure datagram protocols such as User Datagram Protocol (UDP). In the context of IoT devices, where real-time communication and low latency are essential, DTLS can provide a secure way to exchange data without the overhead of a connection-oriented protocol. Implementing DTLS can help ensure the confidentiality and integrity of data transmitted over UDP, making it an ideal security protocol for IoT applications.
3. Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS)
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is an extension of the standard HTTP protocol that adds a layer of encryption using TLS or its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). HTTPS is commonly used to secure web traffic and is essential for protecting sensitive information such as passwords and financial data. When it comes to IoT devices, implementing HTTPS can help ensure that data exchanges between devices and servers are encrypted, preventing eavesdropping or man-in-the-middle attacks.
4. Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT)
Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) is a lightweight messaging protocol that is commonly used in IoT applications for transmitting data between devices. MQTT is designed to be efficient and low bandwidth, making it ideal for IoT devices with limited resources. When implementing MQTT, it’s important to configure authentication and encryption to ensure the security of data exchanges. By using TLS to encrypt MQTT connections, you can protect data from interception and unauthorized access.
5. CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol)
CoAP is a specialized web transfer protocol for use with constrained nodes and constrained networks in the Internet of Things. It is designed for small devices with low power and limited resources that need to send and receive data over the internet. CoAP provides support for secure communication through the use of Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS). By using CoAP with DTLS, you can ensure that data transmitted between devices is encrypted and secure, even in resource-constrained environments.
Conclusion
Securing IoT devices is essential to protect sensitive data and ensure the integrity of connected systems. By implementing strong security protocols such as TLS, DTLS, HTTPS, MQTT, and CoAP, you can safeguard your IoT devices against potential cyber threats. It’s important to stay informed about the latest security best practices and to regularly update firmware and software to mitigate security vulnerabilities. With the right security protocols in place, you can enjoy the convenience and efficiency of IoT devices without compromising on security.
Was this helpful?
0 / 0