How to Use an LM1458 Op-Amp: A Beginner’s Guide
Op-amps, short for operational amplifiers, are essential components in electronic circuits for amplifying signals. The LM1458 is a popular dual general-purpose op-amp that can be used in a wide range of applications. In this beginner’s guide, we will walk you through the basics of how to use an LM1458 op-amp effectively.
Understanding the LM1458 Op-Amp
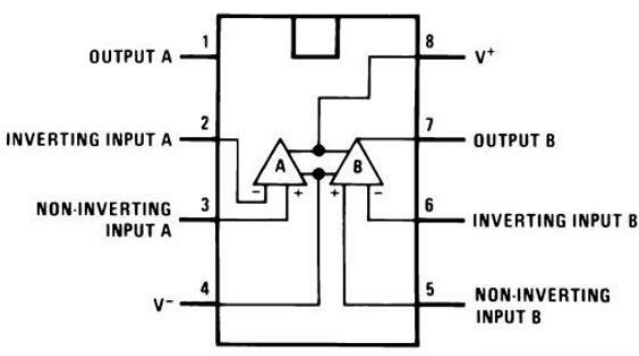
The LM1458 is a dual op-amp that comes in an 8-pin DIP package. It has two amplifiers in one IC, making it convenient for applications requiring multiple amplifiers. Each amplifier has a non-inverting input (marked as +), an inverting input (marked as -), and an output. It is essential to understand the pin configuration of the LM1458 before using it in a circuit.

Basic Connections
To use the LM1458 op-amp, you need to connect it correctly in your circuit. Here are the basic connections you need to make:
- Connect the positive power supply (+V) to pin 8 and the negative power supply (-V) to pin 4.
- Ground pin 3, which serves as the ground for the op-amp.
- Connect the signals you want to amplify to the non-inverting (+) and inverting (-) inputs of the op-amp.
- Connect external components like resistors and capacitors as needed to set the op-amp’s gain and frequency response.
Setting the Gain
One of the essential parameters to consider when using an op-amp is the gain, which determines the amplification factor of the input signal. The LM1458 op-amp has a high gain bandwidth product, making it suitable for high-frequency applications. You can set the gain by using external resistors in the feedback loop of the op-amp.
- For a non-inverting amplifier configuration, the gain is calculated using the formula: Gain = 1 + (R2 / R1), where R1 is the resistor connected between the inverting input and the output, and R2 is the resistor connected between the non-inverting input and ground.
- For an inverting amplifier configuration, the gain is calculated using the formula: Gain = -R2/R1, where R1 is the resistor connected between the inverting input and ground, and R2 is the resistor connected between the inverting input and the output.
Testing the Circuit
Before applying power to the circuit, it is essential to double-check all connections and ensure that there are no short circuits. You can use a multimeter to measure the voltages at different points in the circuit to verify if the op-amp is functioning correctly. Apply power gradually and monitor the output to prevent any damage to the op-amp.
Common Applications
The LM1458 op-amp can be used in various applications, including audio amplifiers, active filters, signal conditioning circuits, voltage followers, and voltage regulators. Its versatility and reliability make it a popular choice for hobbyists and professionals alike.

Conclusion
Using an LM1458 op-amp requires a basic understanding of its pin configuration, connections, and gain setting. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can effectively use the LM1458 op-amp in your circuits and explore its full potential in various applications. Experiment with different configurations and components to unleash the power of this versatile op-amp!
How to Use an LM1458 Op-Amp: A Beginner’s Guide
Op-amps, short for operational amplifiers, are essential components in electronic circuits for amplifying signals. The LM1458 is a popular dual general-purpose op-amp that can be used in a wide range of applications. In this beginner’s guide, we will walk you through the basics of how to use an LM1458 op-amp effectively.
Understanding the LM1458 Op-Amp
The LM1458 is a dual op-amp that comes in an 8-pin DIP package. It has two amplifiers in one IC, making it convenient for applications requiring multiple amplifiers. Each amplifier has a non-inverting input (marked as +), an inverting input (marked as -), and an output. It is essential to understand the pin configuration of the LM1458 before using it in a circuit.

Basic Connections
To use the LM1458 op-amp, you need to connect it correctly in your circuit. Here are the basic connections you need to make:
- Connect the positive power supply (+V) to pin 8 and the negative power supply (-V) to pin 4.
- Ground pin 3, which serves as the ground for the op-amp.
- Connect the signals you want to amplify to the non-inverting (+) and inverting (-) inputs of the op-amp.
- Connect external components like resistors and capacitors as needed to set the op-amp’s gain and frequency response.
Setting the Gain
One of the essential parameters to consider when using an op-amp is the gain, which determines the amplification factor of the input signal. The LM1458 op-amp has a high gain bandwidth product, making it suitable for high-frequency applications. You can set the gain by using external resistors in the feedback loop of the op-amp.
- For a non-inverting amplifier configuration, the gain is calculated using the formula: Gain = 1 + (R2 / R1), where R1 is the resistor connected between the inverting input and the output, and R2 is the resistor connected between the non-inverting input and ground.
- For an inverting amplifier configuration, the gain is calculated using the formula: Gain = -R2/R1, where R1 is the resistor connected between the inverting input and ground, and R2 is the resistor connected between the inverting input and the output.
Testing the Circuit
Before applying power to the circuit, it is essential to double-check all connections and ensure that there are no short circuits. You can use a multimeter to measure the voltages at different points in the circuit to verify if the op-amp is functioning correctly. Apply power gradually and monitor the output to prevent any damage to the op-amp.
Common Applications
The LM1458 op-amp can be used in various applications, including audio amplifiers, active filters, signal conditioning circuits, voltage followers, and voltage regulators. Its versatility and reliability make it a popular choice for hobbyists and professionals alike.

Conclusion
Using an LM1458 op-amp requires a basic understanding of its pin configuration, connections, and gain setting. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can effectively use the LM1458 op-amp in your circuits and explore its full potential in various applications. Experiment with different configurations and components to unleash the power of this versatile op-amp!