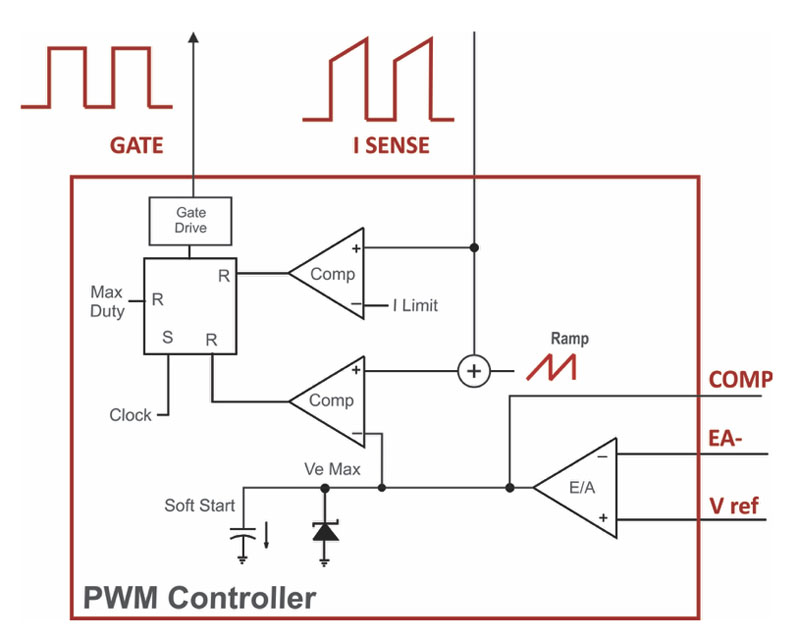
Best Way to Design a PWM Controller
If you’re looking to design a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) controller, you’re in the right place! PWM controllers are widely used in electronic devices to control the speed of motors, the brightness of LED lights, and many other applications. Designing a PWM controller requires a solid understanding of electrical engineering principles and careful attention to detail. In this article, we’ll discuss the best way to design a PWM controller that is efficient, reliable, and effective.
What is a PWM Controller?
Before we dive into the design process, let’s first understand what a PWM controller is. A PWM controller is a device that regulates the power supplied to a load by quickly switching it on and off at a high frequency. By varying the width of the pulses (the on time), the average power delivered to the load can be controlled. This allows for precise and efficient control of devices such as motors and lights.
Design Considerations
When designing a PWM controller, there are several key considerations to keep in mind:
- Frequency: The frequency at which the controller switches the load on and off is crucial. Higher frequencies typically result in smoother control but can also lead to increased power losses due to switching losses.
- Duty Cycle: The duty cycle, or the percentage of time the load is on compared to the total cycle time, determines the average power delivered to the load. It’s important to choose a duty cycle that suits the specific application.
- Control Method: There are various control methods for PWM controllers, including analog control, digital control, and microcontroller-based control. The control method chosen will depend on factors such as cost, complexity, and performance requirements.
Design Steps
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s outline the steps to design a PWM controller:
- Define Requirements: Start by defining the requirements of your PWM controller, including the desired frequency, duty cycle, and control method.
- Select Components: Choose the components for your PWM controller, including a suitable power transistor, inductor, and control circuitry.
- Design Circuit: Design the circuit layout and connections, ensuring that it meets the requirements of your application.
- Prototype and Test: Build a prototype of your PWM controller and test it to ensure it meets the desired specifications.
- Optimize: Fine-tune the design for optimal performance and efficiency, making any necessary adjustments.
Tips for Success
As you embark on designing your PWM controller, here are some tips for success:
- Do thorough research on PWM controller design principles and best practices.
- Seek advice from experienced engineers or mentors in the field.
- Test your design thoroughly to ensure reliability and efficiency.
- Stay updated on the latest developments in PWM controller technology and design.
Conclusion
Designing a PWM controller can be a challenging but rewarding process. By following the best practices outlined in this article and staying informed on the latest advancements in PWM technology, you can create a controller that meets the needs of your specific application. Remember to test your design thoroughly and don’t hesitate to seek help or advice if needed. Good luck on your PWM controller design journey!
Was this helpful?
0 / 0