How to Read a Capacitor Value?
Capacitors are essential components in electronic circuits, used for storing and releasing electrical energy. They come in various shapes and sizes, each with a specific value that indicates their capacitance. Understanding how to read a capacitor value is crucial for choosing the right component for your circuit. In this article, we will discuss the different ways to interpret capacitor values and how to identify them accurately.
Capacitor Markings
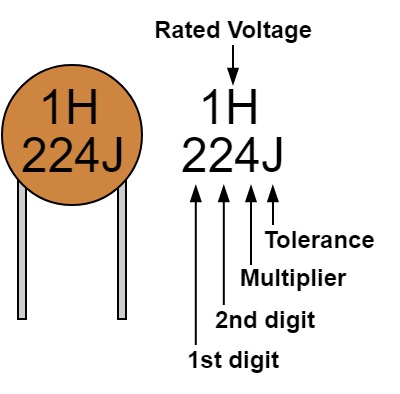
Capacitors are usually marked with alphanumeric codes that represent their capacitance, voltage rating, and tolerance. The capacitance value is measured in farads (F), but most capacitors use smaller units such as microfarads (uF) or picofarads (pF) due to their small size. The voltage rating indicates the maximum voltage that the capacitor can safely handle, while the tolerance specifies the acceptable deviation from the stated capacitance value.
Types of Capacitors
There are different types of capacitors, each with its unique construction and characteristics. Some common types include ceramic capacitors, electrolytic capacitors, film capacitors, and tantalum capacitors. Each type has its own set of markings and codes, making it essential to understand how to interpret them correctly. By knowing the capacitor type, you can easily determine the capacitance value and other specifications.
Reading Capacitor Values
To read a capacitor value, you first need to identify the markings on its body. The capacitance value is typically expressed in uF or pF, followed by a number that indicates the value. For example, a capacitor marked with “104” has a capacitance of 10 x 10^4 pF, which is equivalent to 0.1 uF. Some capacitors may use color coding bands to denote their capacitance value, similar to resistor color codes. It is essential to refer to a capacitor value chart to decode these color bands accurately.
Calculating Capacitance Value
If you encounter a capacitor with no clear markings or codes, you can measure its capacitance using a capacitance meter or multimeter. To calculate the capacitance value, you need to charge the capacitor with a known voltage and measure the time it takes to discharge. By using the formula Q=CV (where Q is charge, C is capacitance, and V is voltage), you can determine the capacitance value of the capacitor accurately.
Choosing the Right Capacitor
When selecting a capacitor for your circuit, it is essential to consider the capacitance value, voltage rating, and tolerance. Make sure to choose a capacitor with the correct capacitance value that meets the requirements of your circuit. Additionally, ensure that the capacitor’s voltage rating is higher than the maximum voltage in your circuit to prevent damage. Lastly, check the tolerance of the capacitor to ensure it falls within the acceptable range for your application.
Conclusion
Reading a capacitor value may seem challenging at first, but with some practice and knowledge, you can easily identify and interpret capacitor markings. By understanding how to read capacitor values accurately, you can choose the right components for your circuits and ensure they function correctly. Remember to refer to datasheets and capacitor value charts for detailed information on specific capacitor types and their markings.
Was this helpful?
0 / 0